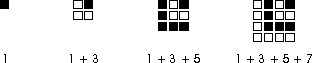STANDARD 11 - PATTERNS, RELATIONSHIPS, AND FUNCTIONS
|
All students will develop an understanding of patterns,
relationships, and functions and will use them to represent and
explain real-world phenomena.
|
Standard 11 - Patterns, Relationships, and Functions - Grades 5-6
Overview
In grades K4 students have been encouraged to view patterns in the
world around them and to use their observations to explore numbers and
shapes. In grades 56 students will expand their use of patterns,
incorporating variables and using patterns to help them solve problem.
The key components of pattern-based thinking, as
identified in the K-12 Overview, involve exploring, analyzing, and
generalizing patterns, and viewing rules and
input/output situations as functions.
Patterns, relationships and functions will become a powerful
problem solving strategy. In many routine problem solving activities,
the student is taught a rote method which will lead to a solution.
Thus, when faced with a problem of the same type he or she just uses
that method to get the solution. In the real world, however, real
problems are not usually packaged as nicely as textbook problems. The
information is vague or fuzzy, some of the information needed to solve
the problem might be missing, or there might be extraneous information
on hand. In fact, a rote method might not exist to solve the problem.
Such problems are generally referred to as nonroutine problems.
Students who are faced with nonroutine problems, and have no
standard method for solving them, often simply give up, because they
do not know how to get started. The ability to discover and analyze
patterns becomes an important tool to help students move forward.
When the students start to collect data and look for a pattern in
order to solve a problem, they are often uncertain about what they are
looking for. As they organize their information into charts or tables
and start to analyze their data, sometimes, almost like magic,
patterns begin to appear, and students can use these patterns to solve
the problem.
Patterns help students develop an understanding of mathematics.
Whenever possible, students in grades
5-6 should be encouraged to use manipulatives to create,
explore, discover, analyze, extend and generalize patterns
as they encounter new topics throughout mathematics. By
dealing with more sophisticated patterns in numerical form, they begin
to lay a foundation for more abstract algebraic concepts. Looking for
patterns helps students tie concepts together, gain a greater
conceptual understanding of the world of mathematics, and become
better problem solvers.
Students in the middle grades should also continue to work with
categorization and classification, particularly in the context
of new mathematical topics, although much less emphasis should be
given to these activities. For example, as students learn about
fractions and mixed numbers, they must identify fractions as being
less than one or more than one, as being in lowest terms or not. They
also apply categorization and classification skills in geometry, as
they distinguish between different types of geometric figures and
learn more about the properties of these figures.
Students in grades 5-6 should begin using letters to represent
variables as they do activities in which they are asked to discover
a rule. They should also begin working with rules that involve
more than one operation. Students at this level describe patterns
that they see by using diagrams and pictorial representations of a
mathematical relationship; some students will be more comfortable
starting with manipulatives and then using a pictorial representation.
Students should record their findings in words, in tables, and in
symbolic equations.
Students in grades 5-6 should begin thinking of input/output
situations as functions. They should recognize that a function
machine takes in a number (or shape), operates with a consistent rule,
and provides a predictable outcome. They should begin to use letters
to represent the number going in and the number coming out, although
considerable assistance from the teacher may be needed.
Throughout their work with patterns, students in grades 5-6 should
use the calculator as a tool to facilitate computation and allow time
for higher level thinking. Teachers should explore its capabilities
with the students and encourage its use, so that students become
proficient.
Standard 11 - Patterns, Relationships, and Functions - Grades 5-6
Indicators and Activities
The cumulative progress indicators for grade 8 appear below in
boldface type. Each indicator is followed by activities which
illustrate how it can be addressed in the classroom in grades 5 and
6.
Building upon knowledge and skills gained in the preceding grades,
experiences in grades 5-6 will be such that all students:
7. Represent and describe mathematical relationships with
tables, rules, simple equations, and graphs.
- Students let the length of one side of a square be 1
unit. They then find the perimeter of one square, two squares
connected along an edge, three squares connected along their edges,
and so forth, as shown below.

They make a table of values and use it to determine a function rule
which describes the pattern. They understand the rule P =
2 x s + 2, where s is the number of
squares, and they use it to predict the perimeter of ten squares.
- Students use a geoboard to model squares with sides of 1,
2, 3, and 4 units. They determine the area and discover the rule for
the area, A = s2, given that s is the
length of the side of a square.
- Students use multilink cubes or base ten blocks to build
rectangular solids. They find the volume of the rectangular solids
(either by counting the cubes or by developing their own shortcuts),
and record the length, width, and height of each solid along with its
volume in a table. They use this information to discover a rule or
formula for finding the volume of a rectangular solid.
- Students find the number of primes between 1 and 100 using
a hundreds chart and applying the process of the Sieve of
Eratosthenes. That is, they first cross out all multiples of 2, then
all multiples of 3, then all multiples of 5, and so on; the numbers
which remain are the primes.
- Students play the secret number calculator game.
One student enters a secret number into the calculator by dividing the
number by itself (e.g., 17 ÷ 17). She then asks her opponent to
guess the number. Each guess is entered into the calculator and then
the equals sign is pressed; the calculator shows the result of
dividing the guess by the secret number. For example, if 17 is the
secret number and 34 is guessed, then the student enters 34 = and sees
2 on the calculator. Play continues until 1 is shown on the
calculator, so that the opponent has guessed the secret number. (Some
calculators will need to have different keys pressed for the same
result, such as 17 ÷÷ 34 =.)
- Students look for the numbers which are palindromes (remain
the same value when the digits are reversed) between any given pair of
numbers. They decide which years in the21st century will be the first
5 palindromes.
- Students determine how much money is earned hourly for a
job mowing lawns or babysitting. They find the amount earned for
working different numbers of hours. They organize the data in chart
or table form. They look for a pattern and write simple equations;
for example, the sentence For babysitting or mowing lawns, I get $5
per hour. translates into the equation E = 5 x
h (Earnings equal five times the number of hours
worked).
- Students use patterns to help them find the value of a
point on a number line between two whole numbers when the number line
is divided into fractional or decimal parts.
- Students investigate patterns involving arithmetic
operations that can be generalized to a mathematical expression with a
variable. For example:
| 1. |
Choose any number |
* |
n |
| 2. |
Multiply your number by 6 |
* * * * * * |
6 x n |
| 3. |
Add 12 to the result |
* * * * * * | | | | | | |
6 x n + 12 |
| 4. |
Take half |
* * * | | | |
3 x n + 6 |
| 5. |
Subtract 6 |
* * * |
3 x n |
| 6. |
Divide by 3 |
* |
n |
| 7. |
Write your answer |
|
n |
- Students use lima beans or other counters to create
trinumbers, the number of beans used for the triangles below.
They try to predict what the tenth trinumber will be and then use this
result to develop the expression (3 x n) for the
nth trinumber.

8. Understand and describe the relationships among
various representations of patterns and functions.
- Using a 4x4 geoboard or dot paper, students create various
sized squares. For each square, they record the length of its side
and its area in a table. Then they show their results as a bar graph
(side vs. area), as ordered pairs (side, area), as a verbal rule
("the area of a square is the length of its side times
itself"), and as an equation (A = s x s,
where s is the length of the side). They repeat this for
rectangles of varying sizes, recording the length and width and
corresponding area in a table. Students discover the pattern and
develop the formula for the area of a rectangle, A = l x
w, by inspecting the numbers in the table.
- Students cut out squares from graph
paper, recording the length of the side of the square and the number
of squares around the border of the square. They look for a pattern
that will allow them to predict the number of unit squares in the
border of a 10 x 10 square and then a 100 x 100 square. They describe
their pattern in words. The teacher then helps them to develop a
formula (4 x n) - 4 for finding the number
of unit squares in the border of an n x n square.
- Students explore patterns involving the sums of consecutive
odd integers (1, 1 + 3,
1 + 3 + 5, 1 + 3 + 5 + 7, ...) by using unit squares to make
Ls to represent each number and then nesting the Ls, as in the
diagram below:
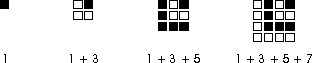
Then they make a table that shows how many Ls are nested and the
total number of unit squares used. They look for a pattern which will
help them predict how many squares will be needed if 10 Ls are nested
(i.e., if the first 10 odd numbers are added together). They make a
prediction and describe how they generated their prediction (e.g.,
when you add the first 3 odd numbers, it makes a square that is three
units on a side, so when you add the first 10 odd numbers, it should
make a square that is ten units on a side and you will need 100
squares). They share their solution strategies with each other and
develop one (or more) expressions, like n x n, that can
be used to find the sum of the first n odd numbers.
9. Use patterns, relationships, and functions to model
situations and to solve problems, in mathematics and in other
subject areas.
- Students use calculators to study fractions whose decimal
expressions repeat, and predict what digit is in any given place.
- Students look at what happens when a ball is hit at an
angle of 45 degrees on a rectangular pocket billiards table. They make a
table that shows dimensions of various tables, initial positions of
the ball, and which pocket, if any, the ball eventually goes
into. They look for patterns which will help them predict which pocket
the ball will go into for other situations.
- Students work in groups to decide how to make a
supermarket display of boxes of SuperCrunch cereal. The boss wants
the boxes to be in a triangular display which is 10 boxes high and one
box deep. Each box is 12 inches high and 8 inches wide. The students
use patterns to help them decide how many boxes they would need and
whether this is a practical way to display the cereal.
- Students look at the fee structure for crossing a toll
bridge near them, such as the Walt Whitman bridge into Pennsylvania or
the George Washington bridge into New York, and use patterns to help
them decide whether it makes sense for someone who works on the other
side of the bridge for 12 days each month to buy a commuter
sticker.
10. Analyze functional relationships to explain how a
change in one quantity results in a change in another.
- Students predict what size container is needed to hold
pennies if, on the first day of a 30-day month, they put in one penny
and double the number of pennies each succeeding day. After making
their predictions, they calculate how many days it will take to fill
thatcontainer, and how many containers like that they would actually
need for the whole month.
- Students make a chart that helps them understand
the charges for a taxi ride when the taxi charges $2.75 for the first
1/4 mile and $.50 for each additional 1/4 mile. They look at rides of
different lengths and figure out how much each trip would cost. Then
they write an explanation of how they found the cost.
- Students look for a pattern between the
temperature in degrees Fahrenheit and degrees Celsius and write an
explanation of that relationship.
11. Understand and describe the general
behavior of functions.
- As a regular assessment
exercise, students fill in Function Machine tables like those
shown below. Sometimes they are given the rule and sometimes they are
asked to find the rule.
|
|
| x | y |
| 5 | 18 |
| 7 | ? |
| ? | 38 |
| 3 | ? |
| y = 4x-2 |
|
|
- Students investigate graphs without numbers. For example,
they may study a graph that shows how far Yasmin has walked on a trip
from home to her friend's house and back, where time is shown on
the horizontal axis and the distance covered is on the vertical
axis. Students tell a story about her trip, noting that where the
graph is horizontal, she has stopped for some reason.
12. Use patterns, relationships, and linear functions
to model situations in mathematics and in other areas.
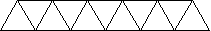
- Students start with a single equilateral triangle with side
of length 1 and find its perimeter. Then they add a second such
triangle, matching sides exactly, to make a train or a wall and find
its perimeter. They continue adding triangles, as in the diagram
below, and find the perimeters of the resulting figures. The students
try to predict the perimeter of ten triangles in a wall and then look
for a function rule which describes the pattern - for example, if
n is the number of triangles, then P = n +
2.
- Students look for as many different ways to make change for
50 cents as they can find. They make a table showing their results
listed in an organized fashion and explain why they think they have
found all of the possibilities.
- Students investigate what happens when they do arithmetic
on a 12-hour clock. They find that 3 + 11 = 2 and that 4 - 6 =
10. They understand that 5, 17, and 29 are all equivalent to 5, and
connect this to the remainder obtained when dividing each by 12.
- Students develop a patchwork quilt design using squares and
isosceles right triangles to make a 12 inch by 12 inch patch. They
use patterns to help them decide how many pieces of each size are
needed in order to complete a 3 foot by 5 foot quilt.
- Students are given the following open-ended assessment
problem: Who will win the 100 meter race between Pat and
his older sister, Terry? Pat runs at an average of 3 meters
per second, while Terry runs at an average of 5 meters per
second. Since Pat is slower, he gets a 25-meter head start.
Use a table or a graph to help you find out who will be the
winner. Then write an explanation of how you solved the
problem and explain what head-start you think Pat should
have.
13. Develop, analyze, and explain arithmetic
sequences.
- Students explore and try to explain the sequence
made by the numbers of diagonals in a series of polygons with
increasing numbers of sides. For example, a triangle has no
diagonals, a square has 2 diagonals, a pentagon has 5 diagonals, a
hexagon has 9 diagonals, and so on. They examine the sequence 0, 2,
5, 9, try to extend it, and justify their conclusion.
- Students read The King's
Chessboard by David Birch. In this old folk tale, which has been
told many times in many languages, a king is undecided about a gift to
give to one of his advisors. Finally he decides that, on one day, the
advisor will receive a single grain of rice on the first square of a
chessboard. On the next day, that amount will be doubled and two
grains will be placed on the second square. On day three, four grains
will be put on the third square, and so on, doubling every day until
the entire board is filled. The students use calculators to figure
out the king's indebtedness on the tenth day, the twentieth day,
and so on.
References
-
Bird, David. The King's Chessboard. Puffin
Pied Piper Books, 1988.
On-Line Resources
-
http://dimacs.rutgers.edu/archive/nj_math_coalition/framework.html/
The Framework will be available at this site during
Spring 1997. In time, we hope to post additional resources
relating to this standard, such as grade-specific activities submitted
by New Jersey teachers, and to provide a forum to discuss the
Mathematics Standards.
|