Robert M. Scher (rscher@dimacs.rutgers.edu)
New York City School Chancellor's theme of "literacy" was implement in math class with a term project in cryptography. Each student was asked to either:
1. do a research paper on cryptography, or
2. invent a code. write a secret message in code. provide a decryption of the message.
Two math fun days were introduced. Cryptologoy puzzles were both handed out and described on the chalk board (hand out attached). Codes covered were:
1. Caesar cipher
2. Rotating grill
3. Rail fence
4. Matrix crypt
5. Pig-pen
6. Columnar transposition
Cryptography supplemental lessons to graphing linear equations
Pre-requisite lessons
1. Basic graphing
2. Graphing equations
3. Graphing by slope-intercept method
4. Inverse equations
Aim: How do we use coding with linear equations?
Do Now
Decode this "secret" message:
x= 23, 8, 1, 20, 19 13, 25 12, 9, 14, 5 ? y= ?
Use the "decoding" equation y= x
x= # on circle
y= # secret letter
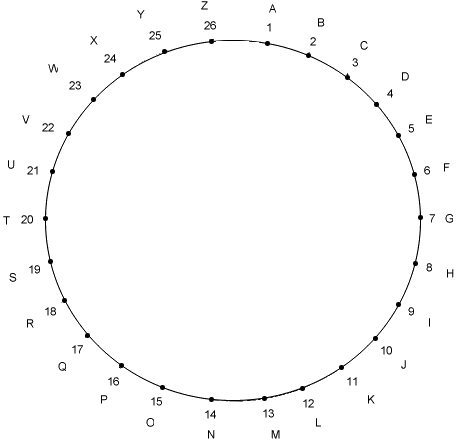
Handout: "coding circle" ditto
Example for discussion
Try this secret message:
PDWK LV IXQ
Discuss the "secret coding" equation
y= x+3
Find the decoding equation by solving for x
Decoding equation
x= y-3
Practice
1. If y= 2x+3 is encoding, what is the decoding equation?
Class Activity
1. Each student writes a 25 letter coded message using a simple
y= x+a equation where
-6 < a < 6
Give each student a different number. Work in pairs coding and decoding.
Topics Covered
Equations
Graphing
Evaluating
Aim: How to use graphing to find a secret in a linear equation.
Do Now
1. Write the equation of the line through points (-3, 3) and (3, 21)
2. Graph the equation.
Handout: Graph paper
Have students number the y axis from 0 to 26. Place the letters A through Z along the y axis beginning with A=1 through Z=26.
There are 2 sets of secret equations:
| 1. y= x+2 | 1. 15x+18 | |
| 2. y= 19x+3 | 2. 4x+9 | |
| 3. y= 9x+1 | 3. 14x+1 | |
| 4. y= 19x+1 | 4. 20x+5 | |
| 5. y= 9x+19 | 5. 9x+19 | |
| 6. y= 24x | 6. 25x |
Students work in pairs. Each pair of students is given 6 papers numbered A1-A6 or B1-B6. Each paper has a pair of points. Students are told to:
1. Write the equation in y =mx+b form
2. Graph the equation
3. Decode the message as follows:
"M" number of A1 is first letter of message. "B" number is second letter of message, etc. Use the y axis to convert #'s to letters.
Use these pairs of points as possible values:
| A1 | (0, 2)(3. 5) | B1 | (-1, 3)(0, 18) | |
| A2 | (-1, -16)(0, 3) | B2 | (1, 13)(-1, 5) | |
| A3 | (-2, 1)(-3, -8) | B3 | (0, 1)(1, 15) | |
| A4 | (0, 1)(1, 20) | B4 | (-1, -15)(0, 5) | |
| A5 | (-1, 10)(0, 19) | B5 | (-1, 10)(-2, 1) | |
| A6 | (1, 24)(0, 0) | B6 | (1, 25)(0, 0) |
Secret messages decode as follows:
A: "Abscissa is x"
B: "Ordinate is y"